Test Objective:
To ensure that the PV system can reliably disconnect from the grid under abnormal voltage conditions, preventing equipment damage and safeguarding grid stability.
Test Method:
Use the KFA310 to output adjustable power-frequency voltage and simulate both overvoltage (e.g., 120% Un) and undervoltage (e.g., 80% Un) conditions. Verify that the protection relay issues a trip command after the configured time delay, and record the actual pickup values and operating time.
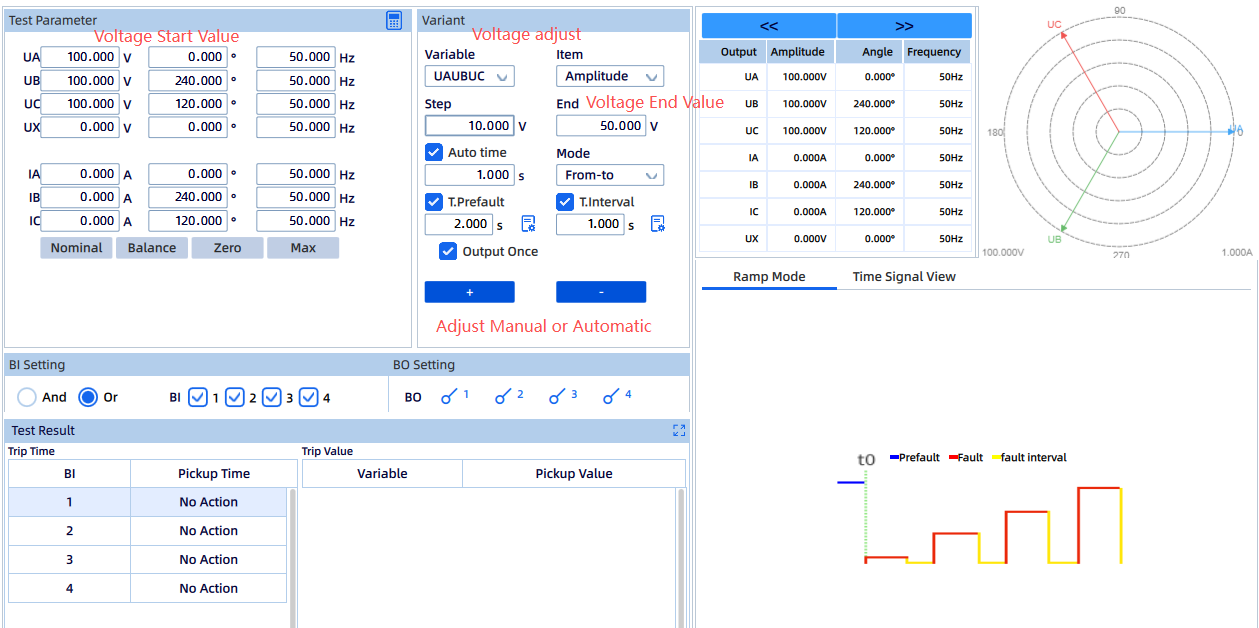
Test Objective:
To verify proper response to grid frequency deviations and prevent PV systems from operating outside nominal frequency limits.
Test Method:
Use the KFA310 to generate variable-frequency voltage signals. Test whether the protection device operates correctly with the specified delay when the frequency exceeds the upper limit (e.g., 50.5 Hz) or drops below the lower limit (e.g., 49.5 Hz).
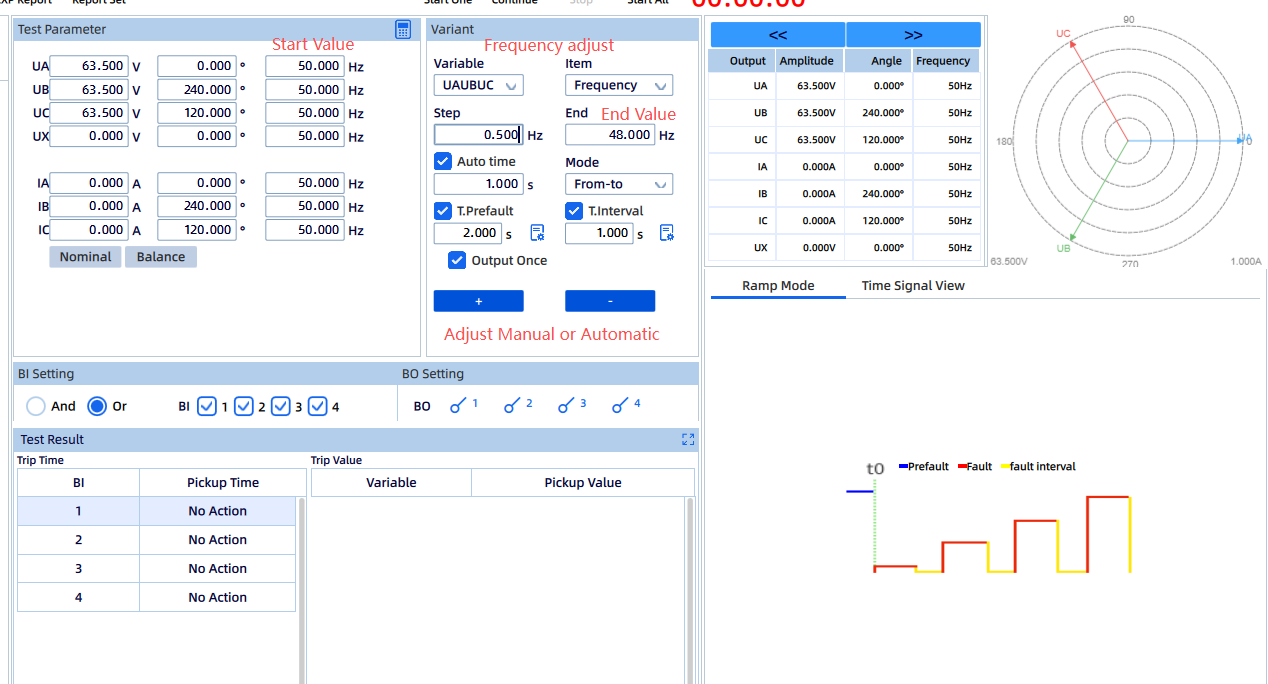
Test Objective:
This is the most critical safety test. When the utility grid is lost, the PV system must detect the islanding condition and cease energizing the line rapidly (typically within 2 seconds) to ensure personnel safety.
Test Method:
Active frequency drift method
Use the KFA310 to simulate the grid and establish normal supply conditions. Then disconnect the KFA310 output to simulate grid outage while connecting a resistive load bank to represent local load. Monitor the inverter output frequency and voltage behavior via the KFA310 to determine whether islanding detection operates correctly.
Passive method
Use the KFA310 to simulate a direct grid voltage loss. Verify that the POI protection relay trips due to voltage and/or frequency abnormality. This test is often combined with over/undervoltage and over/underfrequency protection tests.
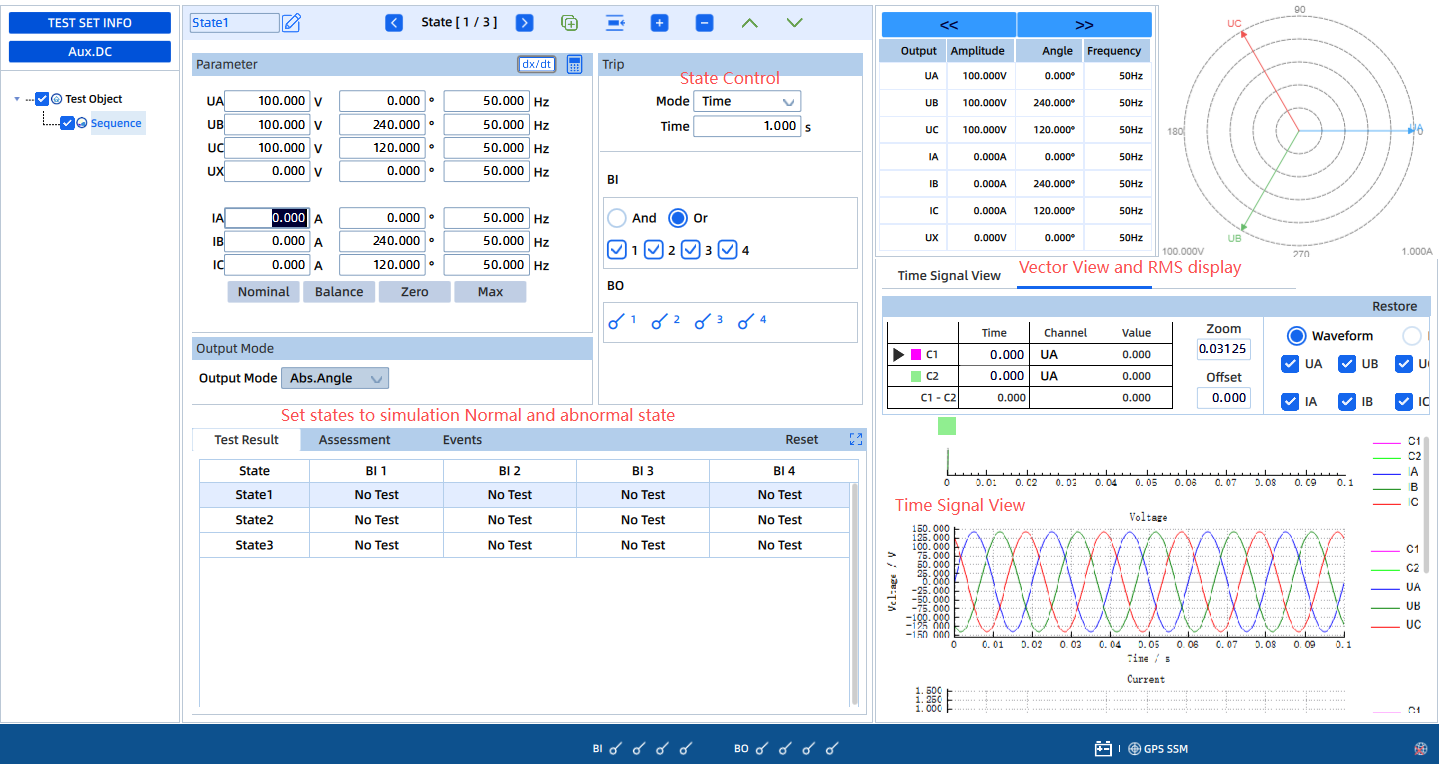
Test Objective:
For self-consumption PV projects where reverse power flow to the upstream grid is not permitted, protection must operate when generated power exceeds local load demand.
Test Method:
Use the KFA310 to simulate system voltage and current. By adjusting the phase angle between voltage and current, simulate reverse power flow from the PV side to the grid side. Verify that the protection relay issues a trip or power-reduction command when reverse power exceeds the set threshold for the defined time delay.
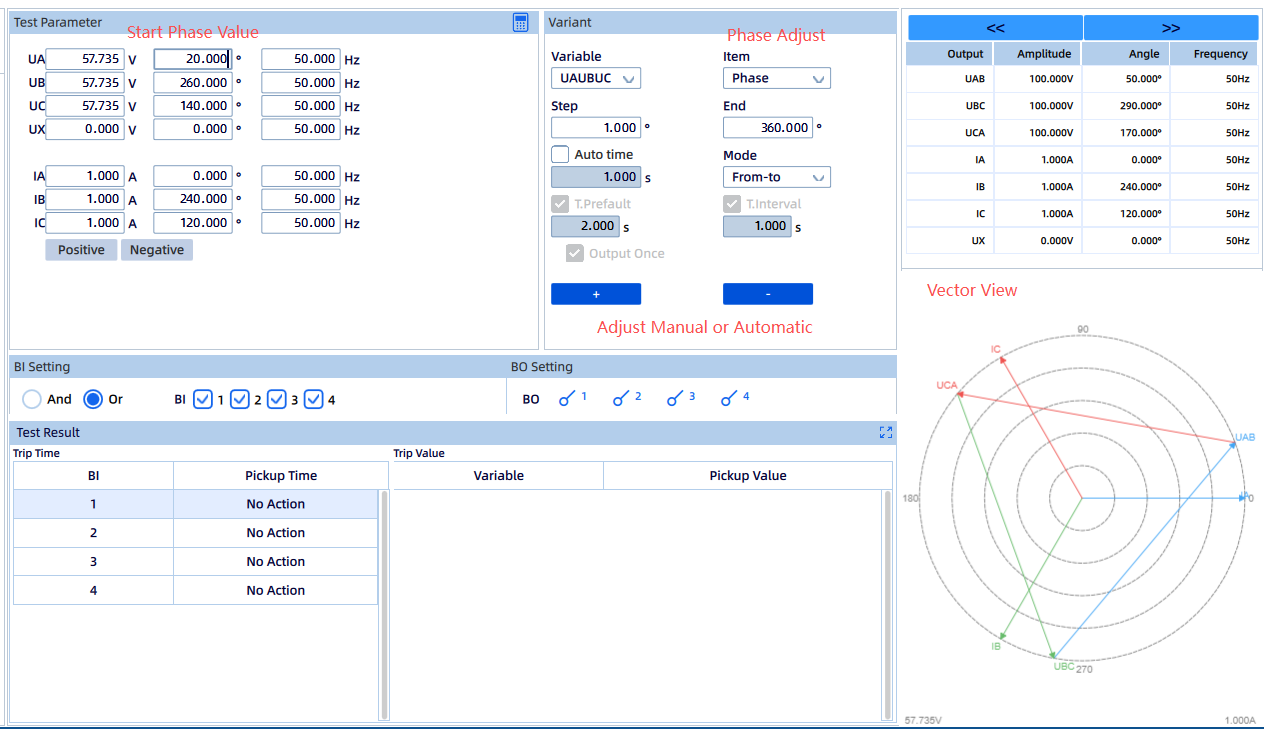
Test Objective:
After grid voltage is restored, the PV system should be able to reconnect safely, either automatically or manually.
Test Method:
Use the KFA310 to simulate grid voltage recovery from zero to nominal value. Verify that the interconnection breaker is permitted to close — or closes automatically — once the “voltage present” condition is satisfied.
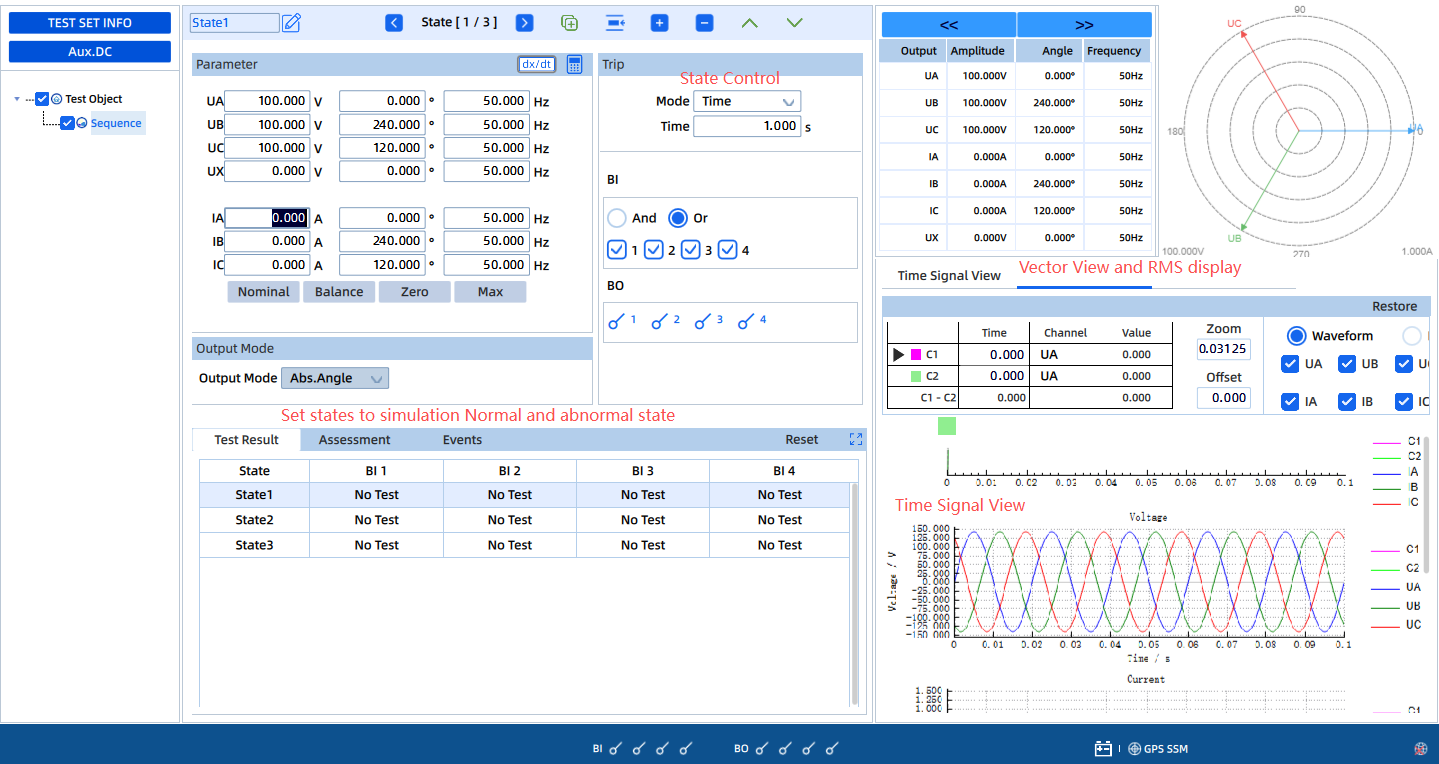
Test Objective:
For medium and large PV plants or projects subject to grid code requirements, verify that the inverter remains connected and supports the grid during short-duration voltage sags.
Test Method:
Use the KFA310 to output voltage sag profiles compliant with national or local grid codes (for example, voltage drops to 20% of nominal for 625 ms). Monitor whether the inverter remains connected. With dynamic simulation capability, the KFA310 can also output reactive current support during the fault ride-through event.
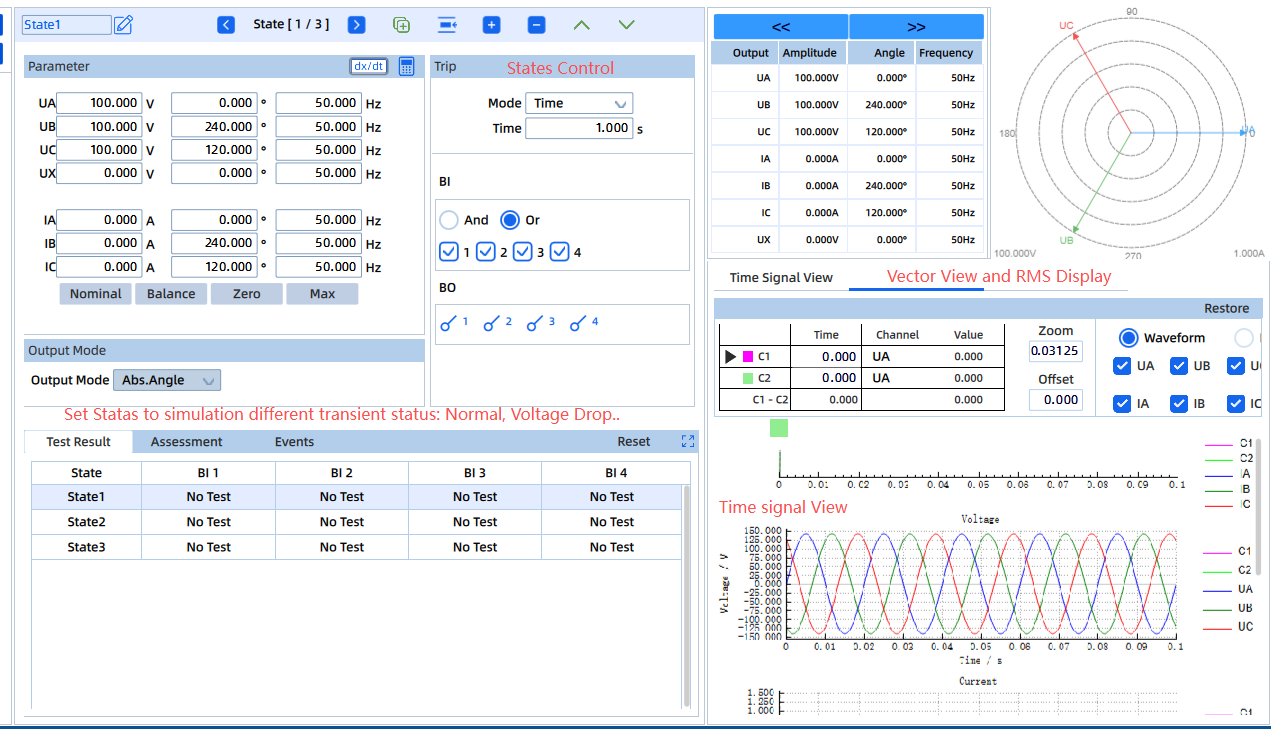
Test Objective:
To verify that built-in inverter protections — such as overcurrent, DC overvoltage, and insulation fault protection — operate correctly.
Test Method:
Trigger inverter alarms or shutdown by adjusting KFA310 AC outputs to simulate AC-side faults, or by coordinating with a DC source to simulate DC-side abnormal conditions. Check actual pickup thresholds and operating times against configured settings.
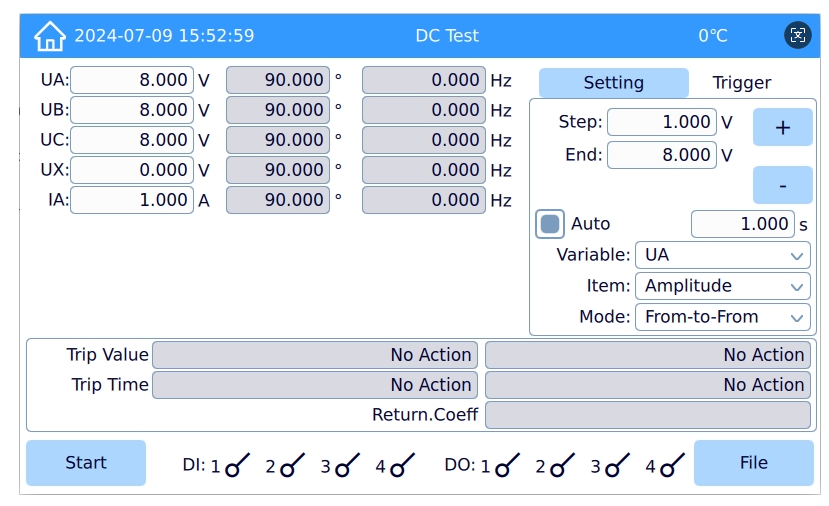
Use the KFA310 digital input/output simulation to generate alarm or fault signals. Verify that SPD status signals are correctly transmitted to the monitoring or SCADA system.
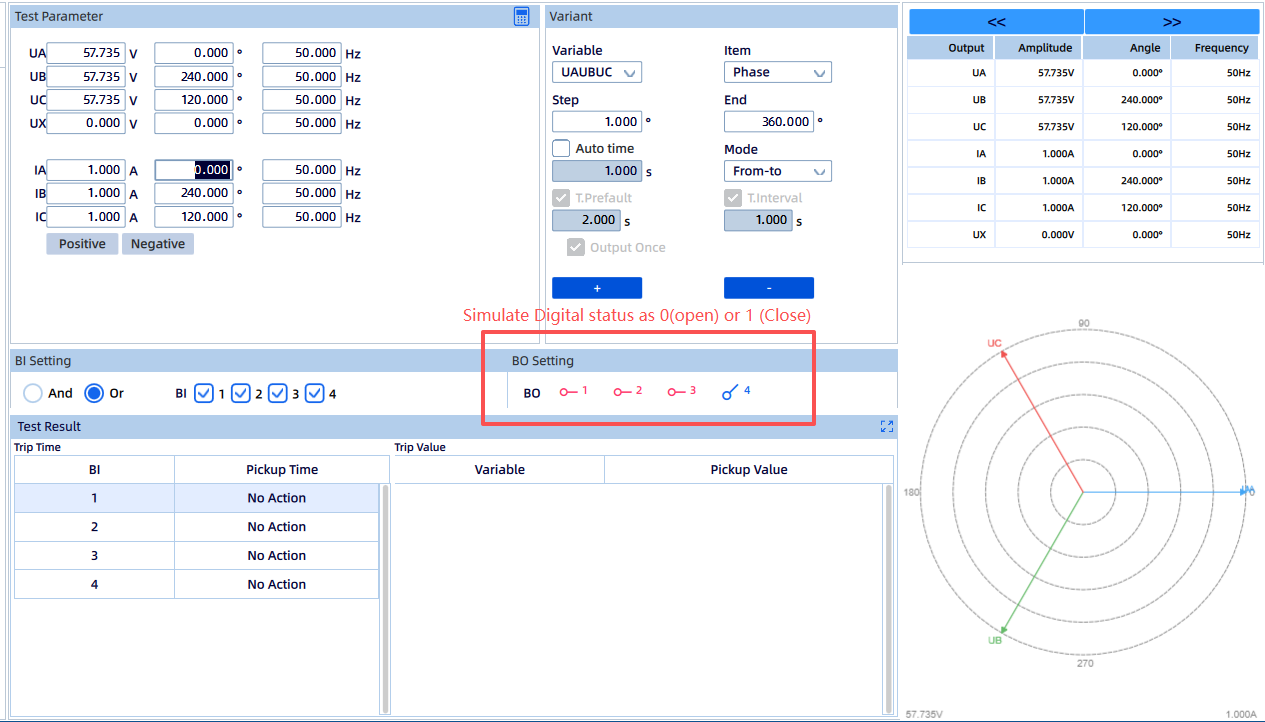
Portable and Flexible:
Compact and lightweight, suitable for low-voltage switch rooms with limited space.
Comprehensive Output Capability:
Standard four-phase voltage and three-phase current outputs, with precise frequency and phase angle adjustment.
Harmonic Generation Capability:
Required for power quality and monitoring device testing.
Strong Software Support:
Built-in test modules for over/undervoltage, over/underfrequency, synchronization, and related functions, with user-friendly operation.